6 Mistakes in Identifying Hydraulic Cylinders
Introduction
Misidentifying cylinders can lead to a range of negative consequences, from reduced operational efficiency and safety risks to unnecessary financial burdens.In the following sections, we’ll dive into each of these mistakes, reveal their impact and outline strategies for avoiding them so you can ensure you’re making the right choice of hydraulic cylinder.
Lack of Understanding Hydraulic Cylinder Specifications
The process of selecting the right hydraulic cylinder for any application begins with a deep dive into its specifications. These technical parameters—bore size, stroke length, rod diameter, and pressure ratings—are not mere numbers; they are the foundational elements that determine how well a cylinder will perform in its designated role.
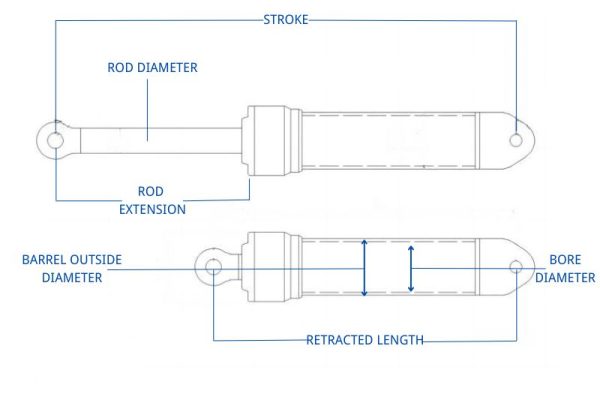
Bore Size
The bore size of a hydraulic cylinder directly influences its ability to generate force. Larger bore sizes allow for more force to be exerted by the cylinder, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications that require substantial power. Conversely, applications that demand finesse and precision might benefit from cylinders with smaller bore sizes, which offer more control and subtlety in operation. Ignoring the bore size or choosing it without consideration to the task at hand can lead to inefficiencies, where the machinery is either too powerful for delicate tasks or lacks the necessary force for heavy-duty operations.
Stroke Length
Stroke length determines the distance a cylinder can extend or retract. This specification is crucial in applications where space is limited or where the extent of movement needs to be precisely controlled. A mismatch in stroke length can lead to situations where cylinders either fall short of completing their intended task or extend beyond the required limits, potentially causing mechanical interference and operational hazards.
Rod Diameter
The diameter of the cylinder’s rod affects its strength and stability, especially in applications where the rod is subjected to side loads. A rod that is too thin may buckle under pressure, while one that is unnecessarily thick can add to the system’s overall weight and reduce efficiency. Selecting the appropriate rod diameter is essential for balancing the demands of strength, stability, and efficiency.
Pressure Ratings
Pressure ratings indicate the maximum hydraulic pressure a cylinder can safely withstand. This specification is critical for ensuring the cylinder’s longevity and reliability, as operating a cylinder beyond its rated pressure can lead to failures and safety hazards. It is paramount to match the cylinder’s pressure rating with the hydraulic system’s operational pressures to avoid the risks of overloading and underperformance.
Ignoring Cylinder Mounting Options
The selection of a hydraulic cylinder does not end with understanding its specifications. The way a cylinder is mounted is equally critical to its performance, integration, and longevity. Mounting styles—such as flange, clevis, and foot mounts—offer different benefits and are designed to meet the varied demands of industrial applications. The choice of mounting style affects not just the cylinder’s operation but also its maintenance, stability, and alignment within the system. Ignoring the importance of matching the cylinder’s mounting option to its intended application can lead to a cascade of operational challenges.
Flange Mounts
Flange mounts are renowned for their strength and rigidity, making them ideal for applications requiring high force and minimal movement. Positioned at the cylinder’s head or cap end, flange mounts distribute stress over a larger area, reducing the risk of misalignment and wear. However, they require precise machining and alignment during installation, underscoring the importance of accuracy in their selection and use.
Clevis Mounts

Clevis mounts offer flexibility and are suited for applications where angular movement is necessary. Attached to the cylinder’s rod end, they allow the cylinder to pivot, accommodating changes in alignment between the load and the actuator. This adaptability makes clevis mounts a popular choice for applications with variable paths of motion. Yet, this very flexibility demands careful consideration of load paths and pivot points to prevent undue stress and wear.
Foot Mounts
Foot mounts provide a stable base for cylinders in stationary applications. They are typically used where the cylinder does not have to withstand significant side loads. The stability offered by foot mounts is advantageous for applications requiring consistent, linear motion. However, without proper support, they can be prone to misalignment and bending forces, which can compromise the cylinder’s efficiency and lifespan.
The Impact of Incorrect Mounting
Choosing the wrong mounting option can severely impact cylinder performance and wear. Incorrect mounts may lead to:
Increased Stress and Wear: Misalignment caused by inappropriate mounting can increase stress on the cylinder’s rod and seals, leading to premature wear and failure.
Suboptimal Performance: A mount unsuited for the application can restrict the cylinder’s movement or force, hindering its performance.
Maintenance Challenges: Incompatibility between the mount and the application can make maintenance more frequent and challenging, impacting operational uptime.
Overlooking Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to corrosive substances significantly impact the longevity and efficiency of hydraulic cylinders. These factors can aggressively wear down components, leading to premature failure if not properly accounted for during the selection phase. Understanding and addressing the environmental challenges can markedly extend the operational life of a hydraulic cylinder, ensuring its reliability and performance.
Temperature
Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can drastically affect the performance of hydraulic cylinders. High temperatures can degrade seals and reduce the viscosity of hydraulic fluids, compromising the cylinder’s efficiency and leading to leaks or failure. Conversely, low temperatures can cause seals to harden and crack, leading to poor performance or even seizing of the cylinder. Selecting cylinders with seals and fluids compatible with the operational temperature range is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity.
Humidity and Water Exposure
In environments with high humidity or direct water exposure, corrosion becomes a significant threat to hydraulic cylinders. Corrosion can weaken structural integrity and lead to leaks or catastrophic failures. Materials such as stainless steel or coatings like chrome plating are often recommended for these conditions to protect against corrosion. Additionally, employing seals that can withstand exposure to water or moisture can further safeguard the cylinder’s operation.
Exposure to Corrosive Substances
Industrial applications may expose hydraulic cylinders to a variety of corrosive substances, including chemicals, salts, and acidic or alkaline materials. These substances can aggressively attack cylinder components, leading to rapid deterioration. Selecting cylinders made from materials resistant to these substances or using protective coatings can prevent corrosion and extend the cylinder’s service life. It’s also important to choose seals and other components that are compatible with the specific chemicals they will encounter.
The Consequences of Neglect
Ignoring the impact of environmental conditions on hydraulic cylinders can have several detrimental effects:
Premature Failure: Cylinders not suited to their operating environment may fail unexpectedly, causing downtime and potential safety hazards.
Increased Maintenance Costs: Frequent repairs and replacements become necessary when cylinders are ill-suited to their environment, driving up maintenance costs.
Operational Inefficiency: Compromised cylinder performance can lead to energy waste, reduced output, and suboptimal system performance.
Neglecting Cylinder Material and Construction
Steel, stainless steel, and aluminum each offer distinct advantages and limitations, making the selection process a critical step in ensuring the cylinder’s suitability for its intended application. Moreover, the construction quality of a cylinder can be the deciding factor between a reliable system and one plagued by frequent breakdowns and inefficiencies.
Material Matters
Steel: Known for its strength and durability, steel is a common choice for hydraulic cylinders in heavy-duty applications. Its robust nature makes it ideal for environments where the cylinder is subject to high loads and stress. However, steel’s susceptibility to corrosion requires protective measures in corrosive environments, adding to maintenance considerations.
Stainless Steel: Offering excellent resistance to corrosion and staining, stainless steel is the material of choice in harsh environments, such as those with high humidity or exposure to corrosive chemicals. While more expensive than standard steel, the longevity and reliability of stainless steel can offset initial costs, particularly in demanding or sanitary applications.
Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, aluminum is favored for applications where weight is a critical factor, such as in aerospace or mobile equipment. Although not as strong as steel, aluminum’s weight advantages can significantly enhance system efficiency and ease of handling.
The Impact of Construction Quality
The best materials can still fall short if the cylinder’s construction is subpar. Quality construction ensures that the materials’ inherent strengths are fully leveraged, leading to a cylinder that performs reliably under the specified conditions. This includes precision in machining, adherence to tolerance specifications, and the quality of welds, all of which contribute to the cylinder’s ability to withstand operational stresses without failure.
Poor construction can lead to a myriad of issues, including leaks, premature seal wear, and structural failures. These issues not only necessitate frequent repairs and replacements but also pose significant safety risks. Therefore, evaluating the manufacturer’s reputation for quality and reliability is as important as assessing the material specifications.
The Consequences of Neglect
Neglecting to consider the material and construction quality of hydraulic cylinders can have significant ramifications:
Reduced Lifespan: Cylinders constructed from unsuitable materials or through inferior processes are more likely to fail prematurely under operational stresses.
Increased Costs: Frequent repairs and replacements due to failure can drive up total ownership costs, negating any initial savings from choosing a less expensive option.
Operational Downtime: Cylinder failures can lead to unexpected downtime, affecting productivity and potentially leading to missed deadlines or compromised safety.
Ignoring Seal Compatibility
Seals are the key to preventing leaks and ensuring that systems maintain pressure integrity and operate efficiently. The wide variety of seals, such as seals, lip seals, piston seals, etc., is a testament not only to the complexity of hydraulic systems, but also to the variety of conditions under which they operate. Each type of seal is designed to perform optimally under specific conditions, including varying pressures, temperatures and different hydraulic fluids.
Understanding Seal Types and Their Applications

O-Rings are versatile and commonly used in hydraulic cylinders for their simplicity and effectiveness in various applications. However, selecting the right material (Nitrile, Viton, etc.) for the O-ring is crucial depending on the hydraulic fluid used and the operational temperature range.
Lip Seals are designed to seal in one direction and are used in applications where unidirectional pressure is prevalent. Their effectiveness is contingent upon the correct orientation and the material’s compatibility with the operating conditions.
Piston Seals come in various designs to handle different pressure levels and directional loads. Their selection is critical in applications where piston speed and pressure vary significantly.
The Impact of Incompatible Seals
Choosing the wrong seal for a hydraulic cylinder can lead to a cascade of problems:
Leakage and Loss of Pressure: Incompatible seals may not provide a tight seal, leading to fluid leakage and a drop in system pressure. This can severely impact the efficiency and performance of the hydraulic system.
Increased Wear and Maintenance: Incorrect seal materials can degrade quickly, especially if exposed to incompatible fluids or extreme temperatures. This necessitates frequent replacements and increases downtime and maintenance costs.
Operational Failures: In severe cases, seal failure can lead to catastrophic system failures, posing safety risks and potentially leading to significant operational disruptions.
Failing to Consider Future Maintenance and Repairability
The longevity and efficiency of hydraulic systems are not solely contingent on their initial performance but also on how well they can be maintained and repaired throughout their operational life. Cylinders that are difficult to disassemble, or for which replacement parts are rare, costly, or altogether unavailable, pose significant challenges. These challenges can lead to prolonged downtime and escalate maintenance costs, adversely affecting overall operational efficiency.
The Importance of Accessible Design
A hydraulic cylinder designed with maintenance in mind features components that are easily accessible for inspection, servicing, and replacement. Such a design simplifies routine maintenance tasks, like seal replacements and cleaning, and reduces the time and labor involved in repairs. This accessibility
The Role of Standardization and Availability of Parts
Selecting cylinders that adhere to industry standards can greatly facilitate the maintenance process. Standardization often means that parts are more readily available and not unique to a specific model or manufacturer, which can significantly reduce lead times for replacements. Furthermore, opting for cylinders from manufacturers with a reputation for supply chain reliability and support can ensure that necessary parts are available when needed, minimizing potential downtime.
The Impact of Modular Design
Cylinders featuring a modular design offer an additional advantage by allowing individual components to be replaced or upgraded without the need to overhaul the entire cylinder. This modularity not only enhances repairability but also provides the flexibility to adapt the cylinder to changing needs or improvements in technology over time.
The Consequences of Neglecting Maintenance and Repairability
Ignoring the future maintenance and repairability of hydraulic cylinders can have several adverse effects:
Increased Operational Costs: Difficulties in maintenance and repair can lead to higher labor costs and the need for specialized tools or services.
Extended Downtime: Waiting for specific parts or dealing with challenging disassembly processes can significantly increase downtime, impacting productivity.
Reduced Lifespan: Inability to perform timely maintenance or repairs can lead to premature cylinder failure, necessitating early replacement and additional costs.
Conclusion
Properly identifying hydraulic cylinders is not a trivial task. It requires a thorough evaluation that includes specifications, mounting options, environmental conditions, quality of materials and construction, seal compatibility, and future maintenance considerations. Avoiding these six common mistakes can significantly improve operational efficiency, safety and cost savings.
We encourage you to learn from your experience or tips for identifying hydraulic cylinders. By sharing knowledge, we can work together to improve the understanding and application of these critical components and move the industries that rely on them forward.
